A paper published last week in the journal Science, written by a team of biologists and atmospheric scientists, expounds on a possible dire future for a range of Arctic animals. It’s called, “Ecological consequences of sea-ice decline” and surprisingly, polar bears are discussed only briefly.
However, with the inclusion of one short sentence, the paper manages to perpetuate misinformation on grizzly/polar bear hybridization that first appeared in a commentary essay three years ago in Nature (Kelly et al. 2010)1. The Post et al. 2013 missive contains this astonishing statement (repeated by a Canadian Press news report):
“Hybridization between polar bears and grizzly bears may be the result of increasing inland presence of polar bears as a result of a prolonged ice-free season.”
Lead author of the paper, Professor of Biology Eric Post, is quoted extensively in the press release issued by his employer (Penn State University, pdf here). In it, Post re-states the above sentence in simpler terms, removing any doubt of its intended interpretation:
“… polar and grizzly bears already have been observed to have hybridized because polar bears now are spending more time on land, where they have contact with grizzlies.”
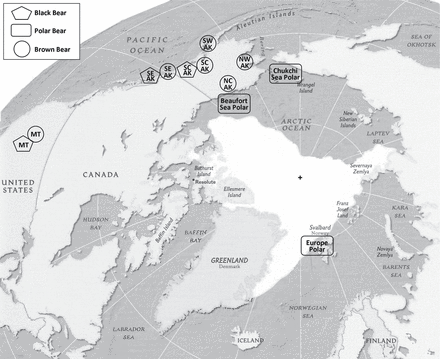
Both statements are patently false. All recent hybridization events documented (2006-2013) occurred because a few male grizzlies traveled over the sea ice into polar bear territory and found themselves a polar bear female to impregnate (see news items here and here, Fig. 1 below). These events did not occur on land during the ice-free season (which is late summer/early fall), but on the sea ice in spring (March-May).
Grizzlies have been documented wandering over the sea ice of the western Arctic since at least 1885 (Doupe et al. 2007; Fig. 2, below) and the presence in this region of hybrid grizzly/polar bear offspring is not an indicator of declining summer sea ice, whether due to global warming or natural causes, or some combination thereof.
Continue reading









You must be logged in to post a comment.