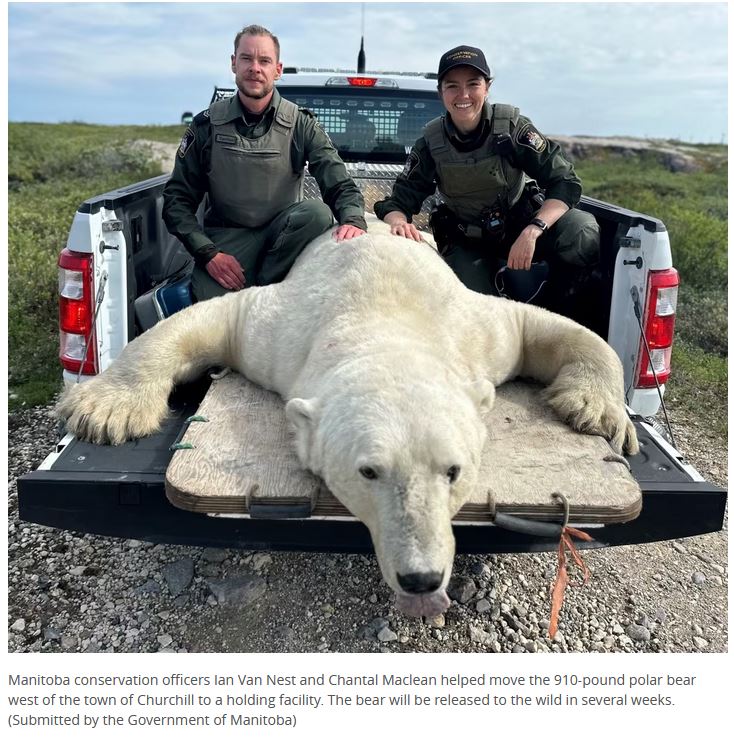
We know transparency’s gone out the window for many public officials, but still: Since early August, I’ve been checking daily for Problem Polar Bear Reports issued by the Churchill Polar Bear Alert Program managed by Manitoba Conservation. This morning (12 September), five reports were posted at once on the Town of Churchill website, dating back to first of the season for the week of August 5-11, see image below.
It’s apparent that the intent of these reports is in part public safety: to raise awareness of the potential threat of wandering polar bears around the town of Churchill because of the language that appears on virtually every report: “stay vigilant”, “be bear smart,” “be bear aware,” etc.
However, the X account for Town of Churchill seems to have been abandoned (last post 19 April 2024), which suggests the town is confident no residents or tourists would benefit from Alerts on X that polar bears are ashore:
The town’s Facebook account seems to be their only method of public communication yet even there, there have been no Polar Bear Alert reports posted this summer.
Oddly, even though it is now apparent from the just-released reports that one bear got so close to town that it had to captured and put in the ‘polar bear jail’ the week of 5-11 August — for the public’s safety — the only safety announcement the town issued that week was a ‘heat warning’ on 12 August:

I guess we are to assume that whoever is running this account – or the town council, or the mayor – believes that a day or two of hot weather (which Churchill gets regularly most years) is more dangerous to public safety than a massive predator wandering around town.
I can only conclude that keeping residents and tourists in the dark about potential threats from local polar bears is one way that Churchill is now adapting to climate change (from CBC News, 10 September 2024):

Bears Onshore and Effective Sea Ice Breakup dates
It is apparent from the wording of the Churchill reports that even by the last week of August this year, all bears were not yet off the ice, since they say only that “most bears” were on shore the week of 26 August to 1 September (see next section).
That suggests the last bears came ashore this year at least a week later than they did in 2020 (at 21 August), which at the time polar bear specialist Andrew Derocher presented as an anomaly (see tweet below). Compare to the situation last year here.
The last report I’ve seen from Derocher (via X) for 2024 on the status of his teams’ tagged females is that many of them (11/29 or 38%) were still on the ice as of 8 August (posted 11 Aug):

Derocher referring to this an “amazing” year that’s “similar” to the 1980s probably doesn’t tell the half of it, since he hasn’t posted any maps since then (as of noon, 12 September).
This effectively keeps secret the date when the last of these females bears actually came ashore, which is in any case a biased microcosm of the entire subpopulation. In other words, we can expect that if 40% of tagged female were still on bits of remnant ice at 8 August, there will have been many more bears, especially males, out there as well – which of course he never mentions.
He also never mentions that satellites under-report the amount of ice at this time of year by as much as 20% because of the effects of melt-water sitting on ice, but we’ve come to expect that.
Oddly, a recent study tried to explain the importance to survival of the recent phenomenon (since about 2015 or so) of bears staying out on melting bits of remnant ice rather than heading immediately to shore when the ice coverage over Western Hudson Bay drops below 50%. They suggested this behaviour was largely confined to male bears because they had to make up for feeding missed during the breeding season (McGeachy et al. 2024).
Females, alternatively, appear to respond to break-up in WH by coming onshore approximately 3 weeks after the mean ice concentration in WH reached 50%, … However, suitable habitat was still present elsewhere in the Bay and appeared to be used by a portion of WH prime age males. [McGeachy et al. 2024: 494, where “prime age males” are aged 5-19 years.]
However, these authors never mention the data reported by Derocher every year showing fairly significant numbers of tagged females lingering on tiny chunks of ice well into August, even though Derocher is a co-author. Funny, that.
Problem Bear Reports 2024, Weeks 1-5
Week 1, 5-11 August
Week 2, 12-18 August
Week 3, 19-25 August
Week 4, 26 August-September 1
Week 5, 2-8 September
References
McGeachy, D., Lunn, N.J., Richards, E.S. and Derocher, A.E. (2024). Sea ice influence on male polar bear survival in Hudson Bay. Arctic Science 10, 483-498. https://doi.org/10.1139/as-2023-004 Open access.





















You must be logged in to post a comment.