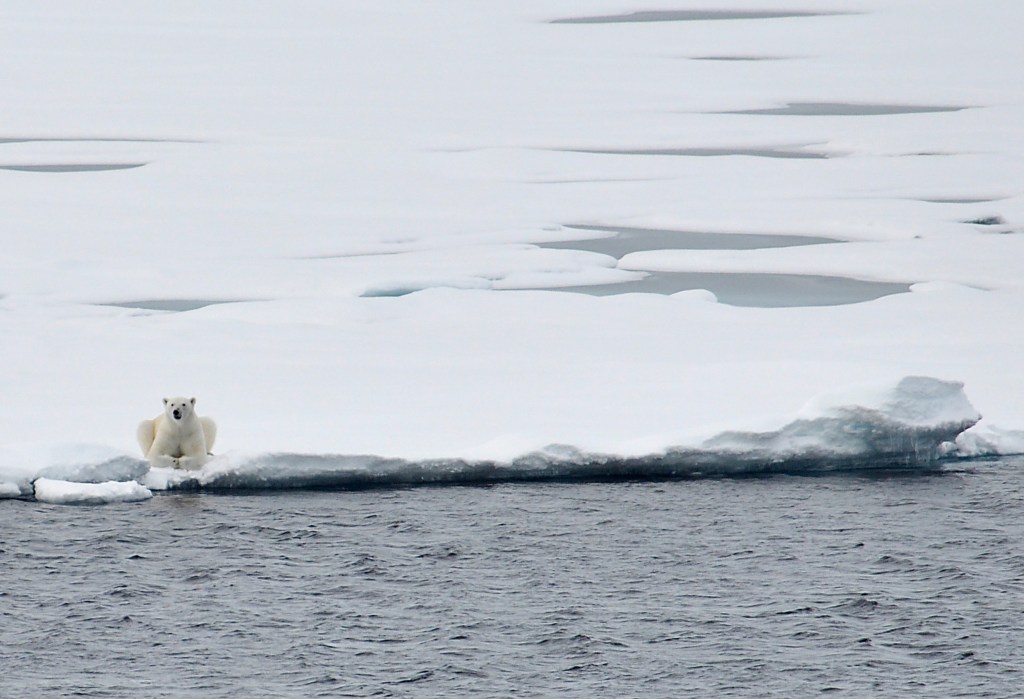
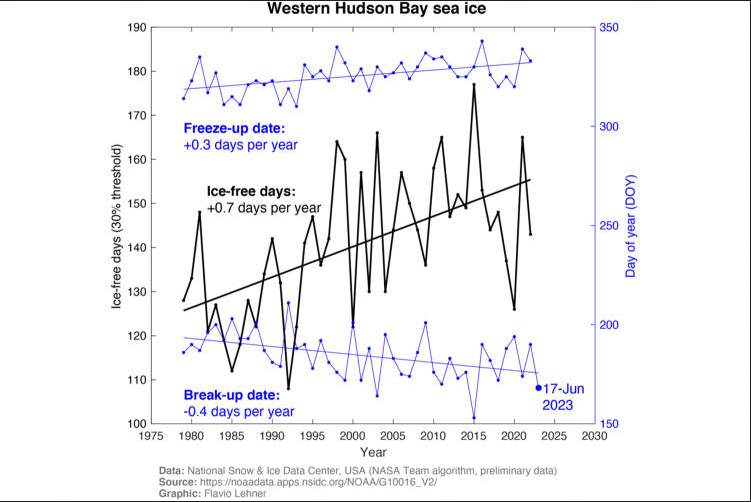
This is an early breakup year for Hudson Bay but sea ice loss has not been accelerating. While some Western Hudson Bay bears have been on land for weeks, others are still out on melting remnants of sea ice, much of it invisible to satellites. This is only the third year since 2014 that the bay has had less than usual amounts of ice, which means most years since then have had normal or nearly normal ice coverage, similar to the 1980s. Hardly the ever-worsening catastrophe of sea ice loss story being spun in the media for Western Hudson Bay polar bears.
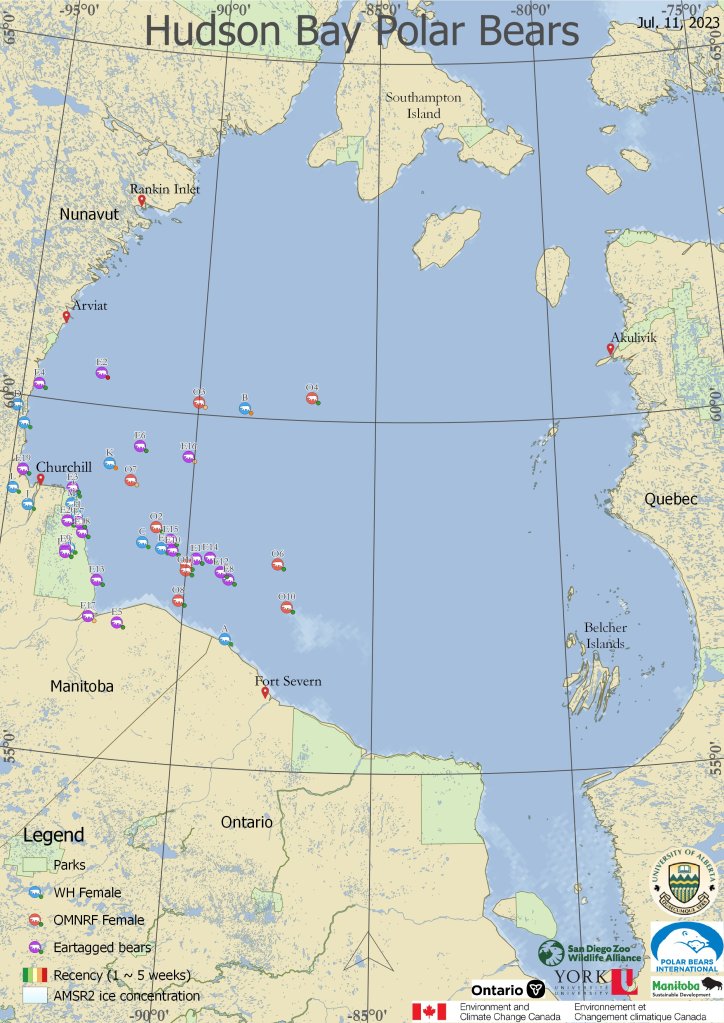
From the tracking map above, out of the 38 visible tags or collars on bears at 11 July 2023, 16 bears (42%) were on land and 22 (58%) were still out on the sea ice. That’s virtually identical to the 40/60 percent split last week when there was even more ice.
Continue reading













You must be logged in to post a comment.