Last week, a senior producer at CBC News, in order to concoct a timely story for ‘Earth Day’, attempted to explain the high number of sightings of polar bears this April in Newfoundland and Labrador, compared to the last two years, as a consequence of climate change and its handmaiden, loss of Arctic sea ice.
Title: ‘With an extinction threat looming, no wonder polar bears are at our door — and on the roof: there’s a grim reason why polar bears have been frequently showing up in coastal communities’. CBC News, 23 April 2022
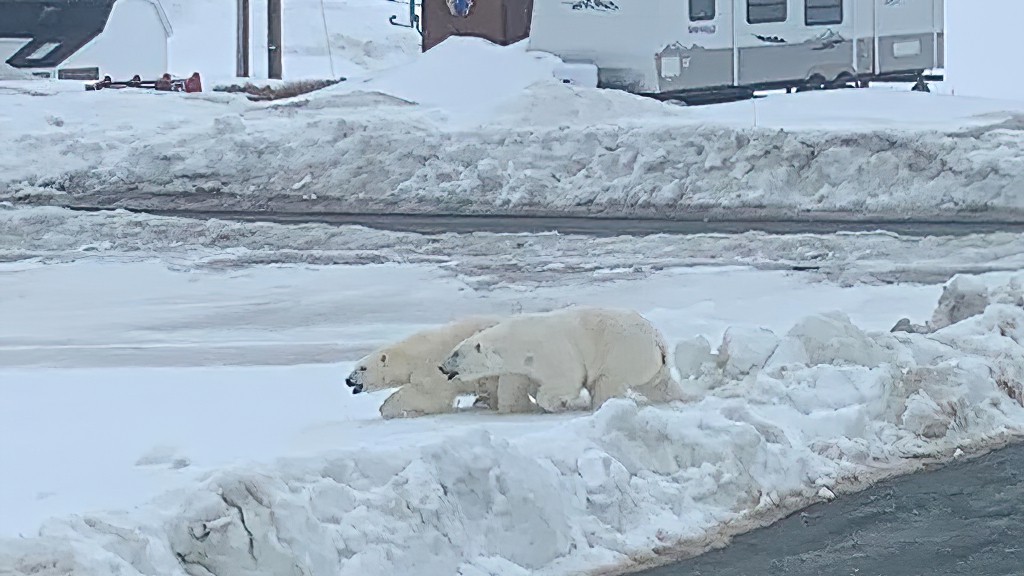

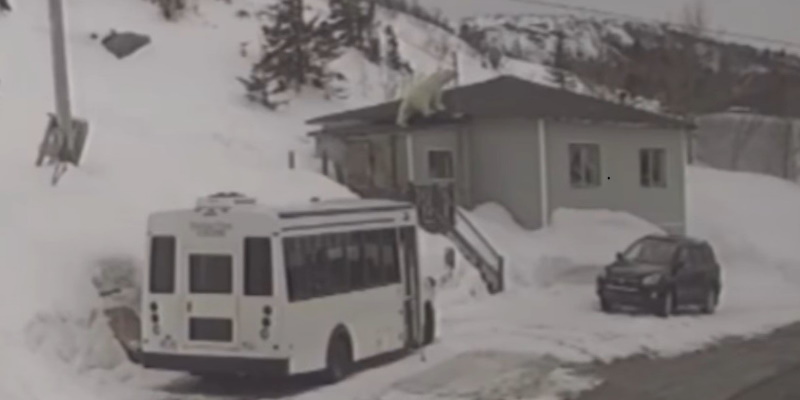
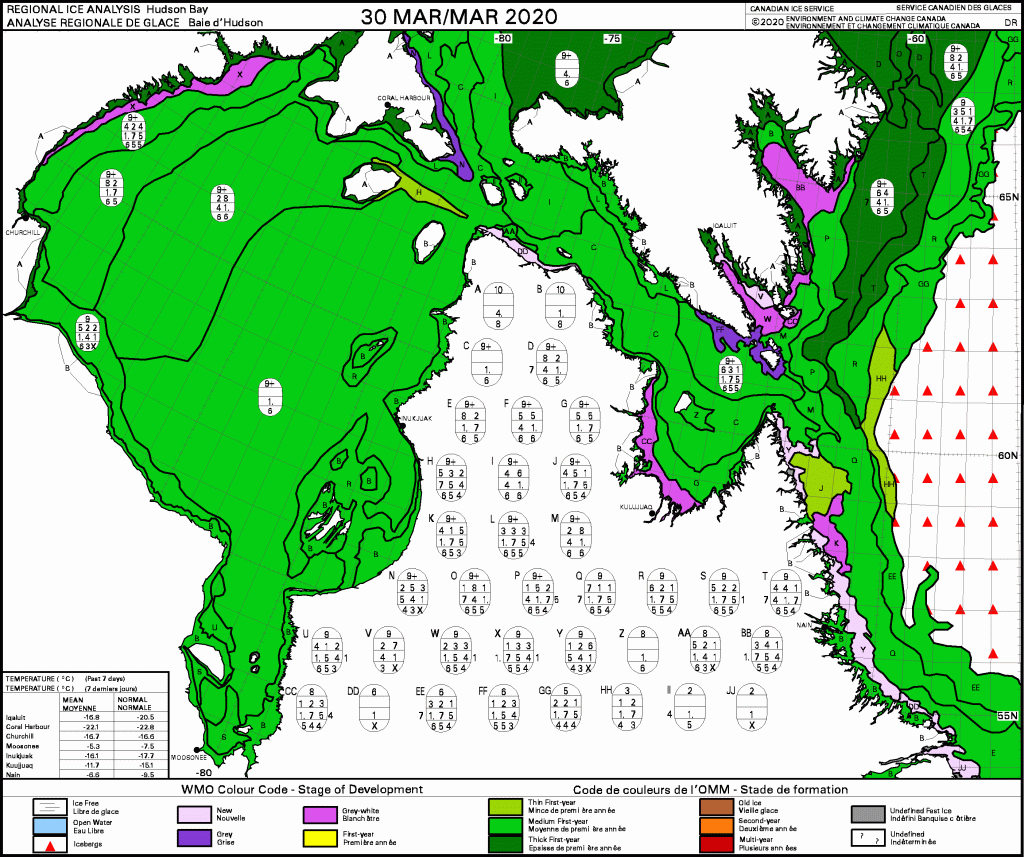
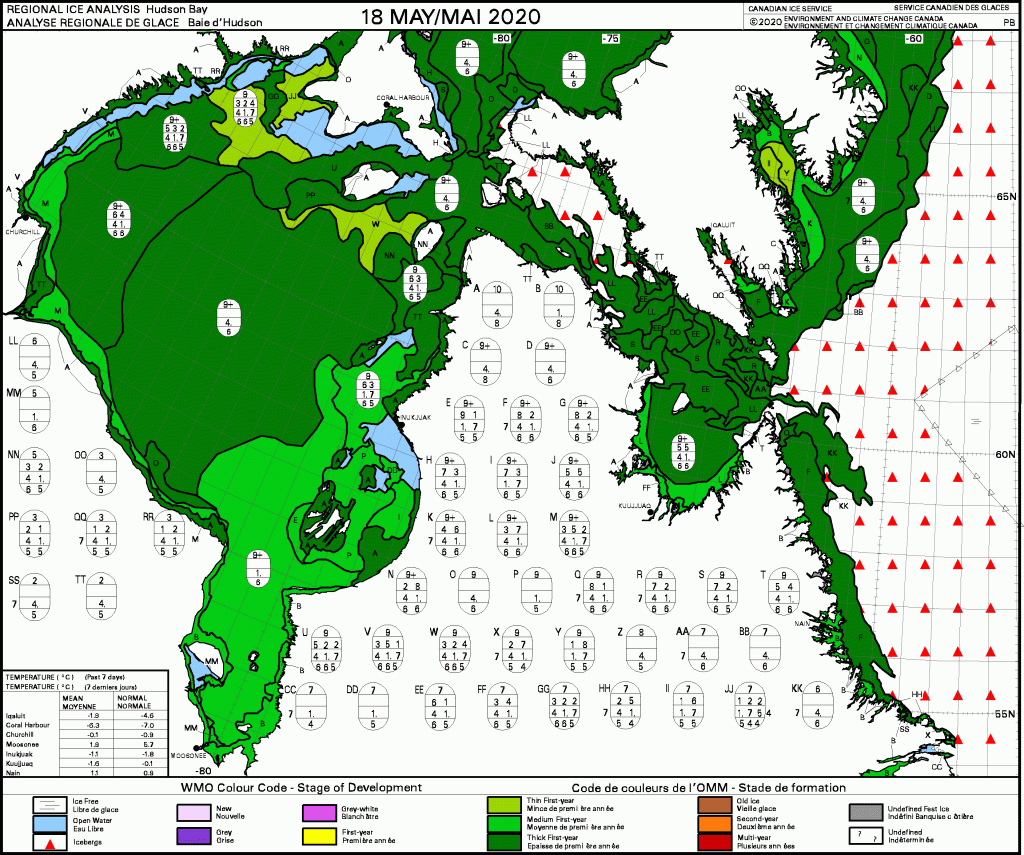
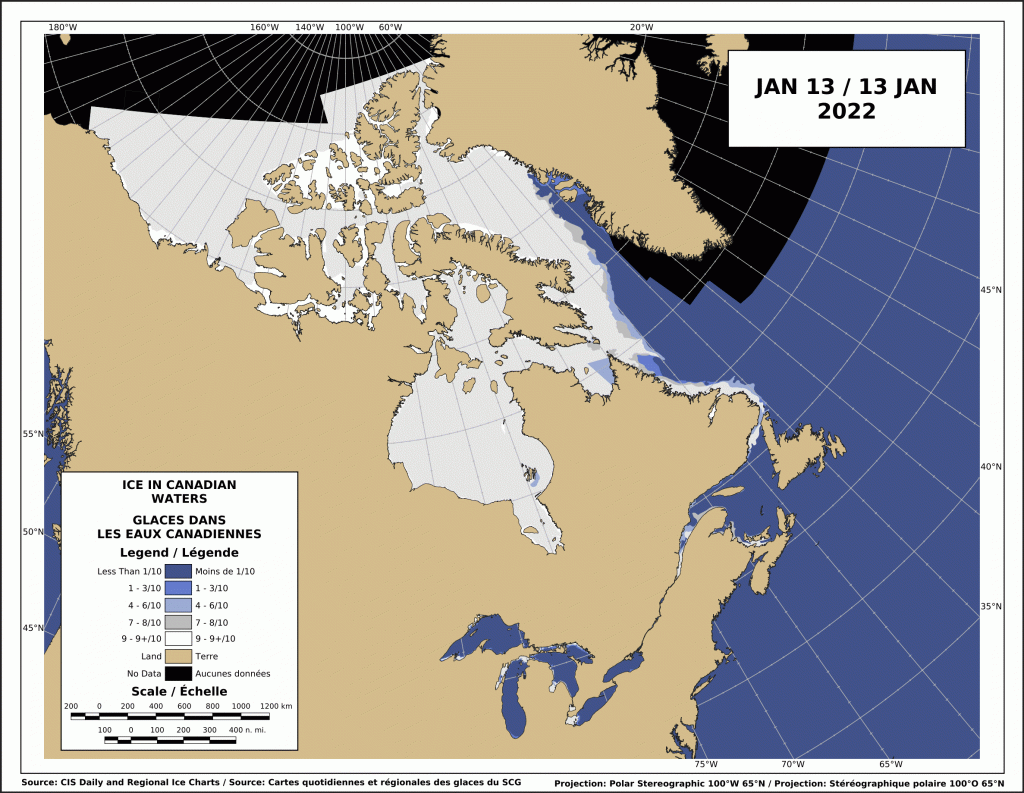
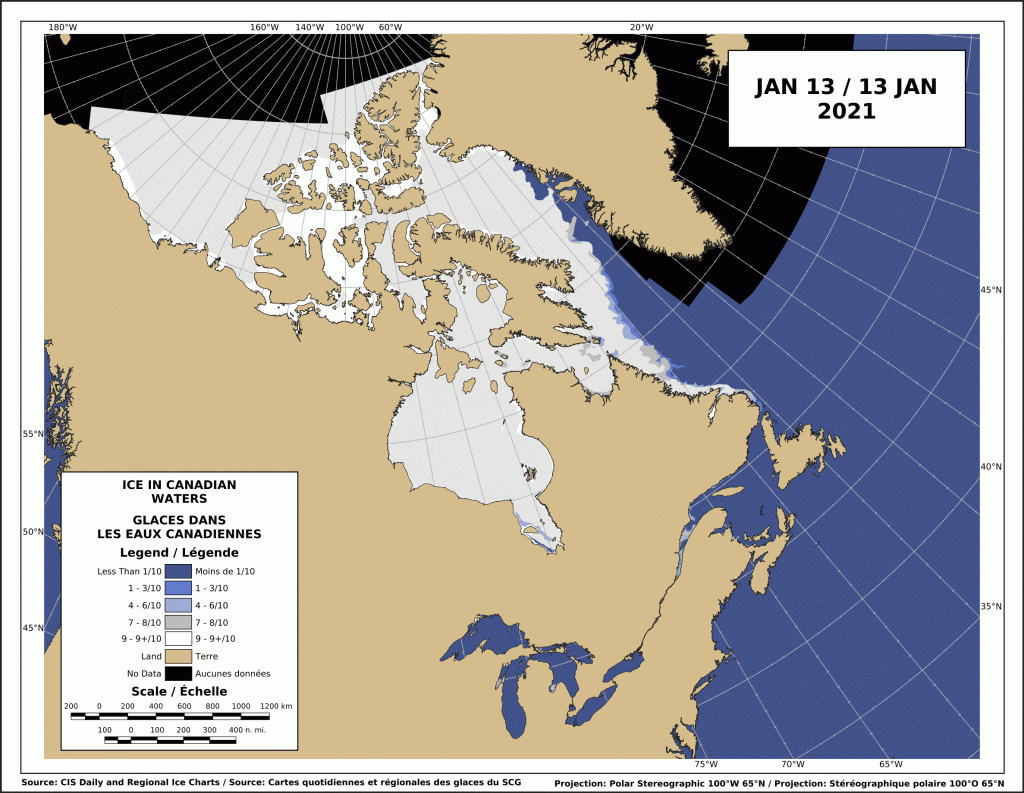
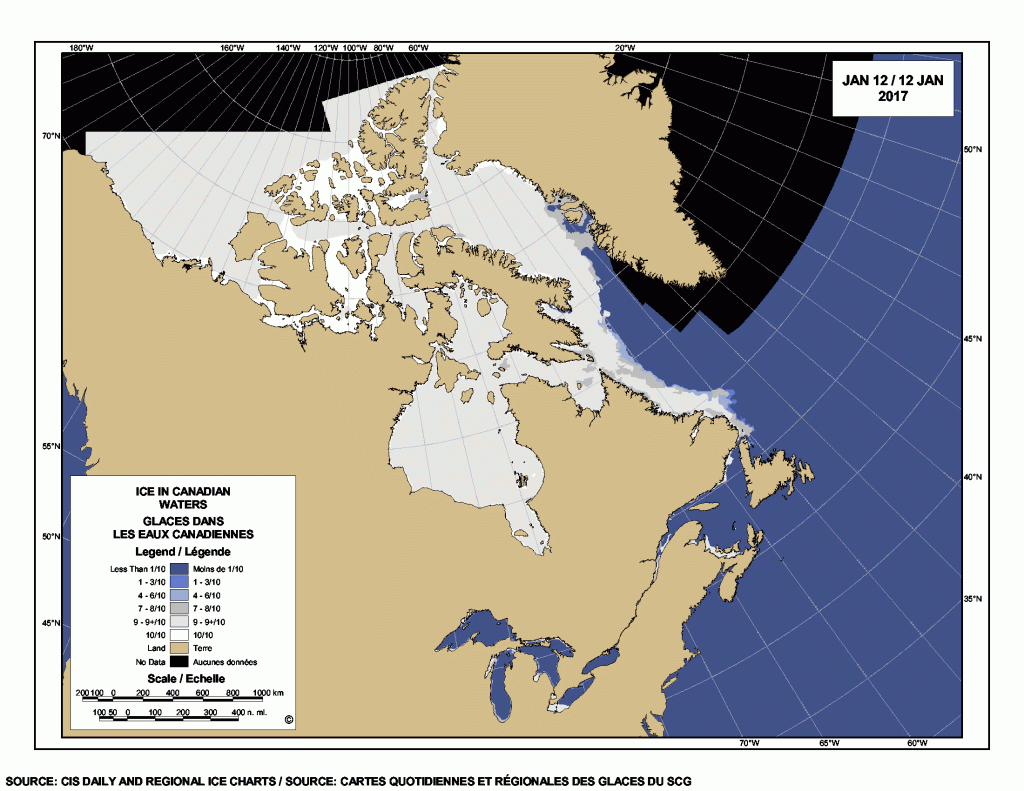
The problem with this narrative is that the East Coast had much reduced sea ice in 2021 and virtually no polar bear sightings in Newfoundland and none in Labrador. There was more ice in 2020 than 2021 but also few bears. This year, ice extent was similar to 2020 for most of the region but polar bear sightings were up considerably.
In fact, the two years with the most sightings and problems with polar bears since 2008 were 2017 and 2018: in 2017, sea ice was exceptionally thick in April (although average in extent) and by June the sea ice was so thick and enduring that the Newfoundland fishing fleet couldn’t get out for spring openings; 2018 was another year of average sea ice extent and had even an even larger number of sightings than 2017, in Newfoundland especially (Crockford 2019:32). This suggests the sea ice vs. polar bear correlation on the East Coast since 2008 – if there even is one – may be the opposite of that stated in the CBC article: less ice usually means fewer bears onshore in Newfoundland and Labrador and more ice often means more bears.
Continue reading











You must be logged in to post a comment.