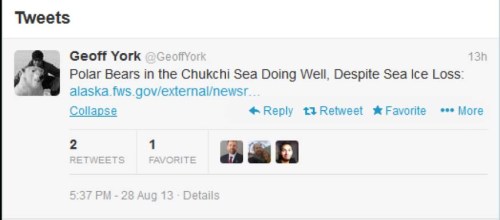
A new peer-reviewed report (Rode et al. 2014 [in print] 2013, accepted), released last month (announced here), documents the fact that polar bears in the Chukchi Sea are doing better than virtually any other population studied, despite significant losses in summer sea ice over the last two decades – even though the Polar Bear Specialist Group (PBSG) said this population was declining (Obbard et al. 2010).

Rather than this good news being shouted far and wide, what we’ve seen so far is a mere whisper. The strategy for suppressing the information appears to have several parts: make it hard to find; don’t actively publicize it; down-play the spectacularly good nature of the news; minimize how wrong they were; keep the focus on the future.
Something similar happened with the newly-published paper on Davis Strait bears (Peacock et al. 2013, discussed here and here) but the news there wasn’t quite so shockingly different from expected. The suppression of good news stands in marked contrast to anything with a hint of bad news, which gets reported around the world — for example, Andrew Derocher and colleagues and their “prepare now to save polar bears” policy paper in February, 2013.
US Fish & Wildlife biologist Eric Regehr, co-investigator of the Chukchi study and co-author of the newly-published report, wrote an announcement about the paper. It wasn’t a real press release, since it was not actually sent to media outlets. It was a statement, with a brief summary of the paper, posted on a regional US Fish & Wildlife website, with no mention of lead author Karyn Rode. Not surprisingly, lack of active promotion = no media coverage.
The posted announcement also down-played how well the Chukchi bears are doing. In fact, the news documented in the paper is much better than any of them let on: Chukchi polar bears are doing better than virtually all other populations studied.
But Regehr also had to do some damage control to counter the evidence this paper contains of how wrong they had all been — not only about the Chukchi population today but about their predictions for polar bears in the future.
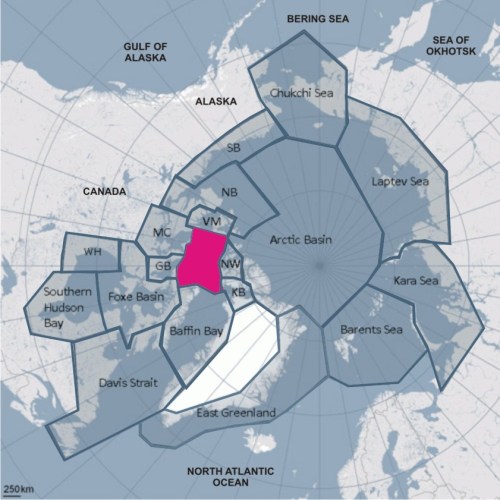
After all, the computer models used to predict a dire future for polar bears combined the Chukchi Sea with the Southern Beaufort, as having similar ice habitats (“ice ecoregions”). The published paper and Regehr’s statement now say these two regions are very different and that polar bear response to loss of sea ice is “complex” rather than a simple matter of less summer ice = harm to polar bears. Regehr goes on to say that polar bear scientists expected this would happen. I call total BS on this one, which I explain in full later (with a map).
Finally, Regehr’s statement emphasizes that good news for 1 subpopulation out of 19 today should not be celebrated because the overall future for polar bears — prophesied by computerized crystal balls — is bleak. Focus on the future, they say. Did they forget that for years they’ve been telling us that polar bears are already being harmed and that this foreshadows what’s to come? Now we have the results of yet another peer-reviewed study showing bears not being harmed by declines in summer ice (see the full list here).
So, in the end, all of this double-talk and contradiction is not just about suppressing this particular paper. There’s much more at stake.
The Rode et al. Chukchi paper is strong evidence that their predictions of a grim future for polar bears – based on theoretical responses to summer sea ice declines that should already be apparent – have been refuted by their own studies. It’s no wonder they want to keep the media away from this story.
Details below. [Update September 11, 2013: another news outlet picks up the story, see Point 2 below]
Continue reading












You must be logged in to post a comment.