Ten years of summer sea ice levels expected to kill 2/3 of the world’s polar bears by 2050 instead saw polar bear numbers grow. And this year, there are also two fabulous books about polar bears and their outstanding success story to celebrate on International Polar Bear Day (Monday 27 February 2017).

One is suitable for kids (Polar Bear Facts & Myths) and another for adults and teens who want the details (Polar Bears: Outstanding Survivors of Climate Change) – see the right sidebar to buy on Amazon or my author website for details on all additional formats. A couple of excerpts from them are below.
So forget turning down your thermostat in a pointless gesture to “reduce your carbon emissions and help polar bears” — as Polar Bears International advocates for Polar Bear Day. Instead, treat yourself or a friend and order a book with a rational approach to species survival.
Speaking of species survival, think about the inconsistency in how some species are treated according to the US Endangered Species Act (ESA). Humpback whale numbers recovered after decades of protection; in 2016, after the state of Alaska filed a petition to delist, most populations were officially removed from the ESA list of ‘threatened’ species.

Humpback whale and calf, NOAA image.
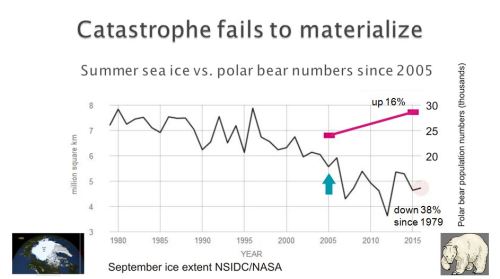
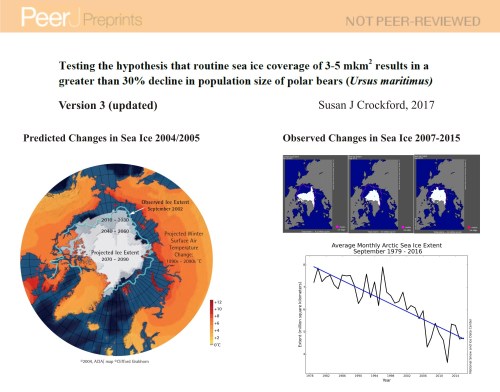
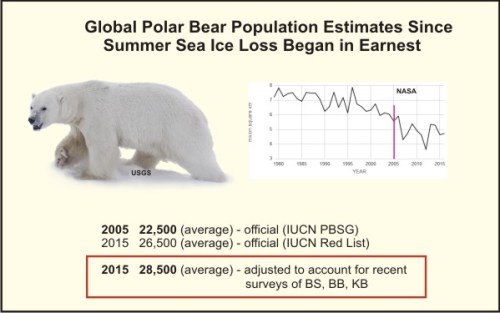
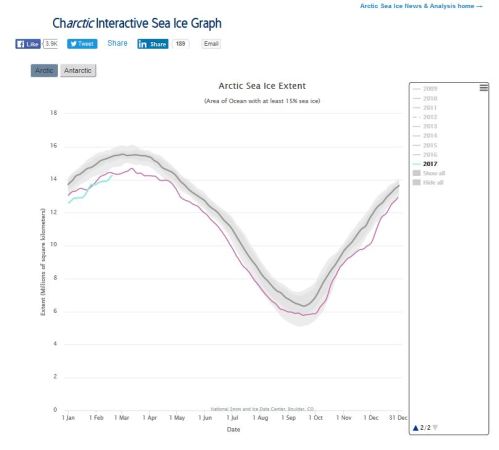
In contrast, by 2015, polar bear numbers had also recovered despite years of low sea ice loss not predicted until 2050, yet remain officially ‘threatened’ with extinction.

Fat bear family at Kaktovik, Alaska (Southern Beaufort), April 2016. USGS photo.
US National Marine Fisheries Service defended the delisting of humpback whales against activists who insisted human-caused global warming threatened the species, but the US Fish and Wildlife Service defends flawed polar bear prophesies.
My books lay out the polar bear success story: in simple form for younger readers and in detail for others. See the excerpts below.

Polar bears have not been driven to the brink of extinction by global warming. In fact, they are thriving (see my final conclusions on pg. 30 of Polar Bears: Outstanding Survivors of Climate Change, above and pg. 32 of Polar Bear Facts & Myths below.

If you’d like to support my efforts to bring this to everyone’s attention, please consider buying a copy or two of my books. If you’ve already done so, keep in mind that your local library might be glad to have copies donated. They also make great gifts.
Save
Save















You must be logged in to post a comment.