The BioScience paper “Internet blogs, polar bears, and climate-change denial by proxy” (Harvey et al. 2018) is a smack-talk response to my pointing out that polar bear numbers did not plummet as predicted when mid-century-like sea ice conditions arrived unexpectedly in 2007 (Crockford 2017). Here is why this shoddy piece of work will go down in history as a self-inflicted wound for the polar bear community (and biologist co-authors Ian Stirling and Steven Amstrup) and an own-goal for their wanna-be climate-hero friends, Stephan Lewandowsky, Jeff Harvey, and Michael Mann.
 “…absolutely the stupidest paper I have ever seen published” tweeted climate scientist Judith Curry, Emeritus Professor of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences at Georgia Institute of Technology (“Georgia Tech”).
“…absolutely the stupidest paper I have ever seen published” tweeted climate scientist Judith Curry, Emeritus Professor of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences at Georgia Institute of Technology (“Georgia Tech”).
Dr. Curry is a favourite target of colleague Michael Mann’s penchant for derogatory name-calling. Ironically, Mann often promotes something he calls the “Serengeti Strategy,” which he described to US Congress in 2017 in presenting himself as a victim of abused by others [my bold]:
“I coined the term “Serengeti Strategy” back in 2012 in “The Hockey Stick and the Climate Wars” to describe how industry special interests who feel threatened by scientific findings—be it tobacco and lung cancer, or fossil fuel burning and climate change—single out individual scientists to attack in much the same way lions of the Serengeti single out an individual zebra from the herd. In numbers there is strength, but individuals are far more vulnerable. Science critics will therefore often select a single scientist to ridicule, hector, and intimidate. The presumed purpose is to set an example for other scientists who might consider sticking their neck out by participating in the public discourse over certain matters of policy-relevant science.” Michael Mann, 2017 Congressional testimony.
Mann thinks others are using this strategy against him but if he had half an ounce of self-awareness he’d see it’s exactly what he and his long list of colleagues are doing with the Harvey et al. BioScience attack on me. Intimidation by numbers is the only rational explanation for a roster of 14 when two incompetent researchers could have produced a similar result.
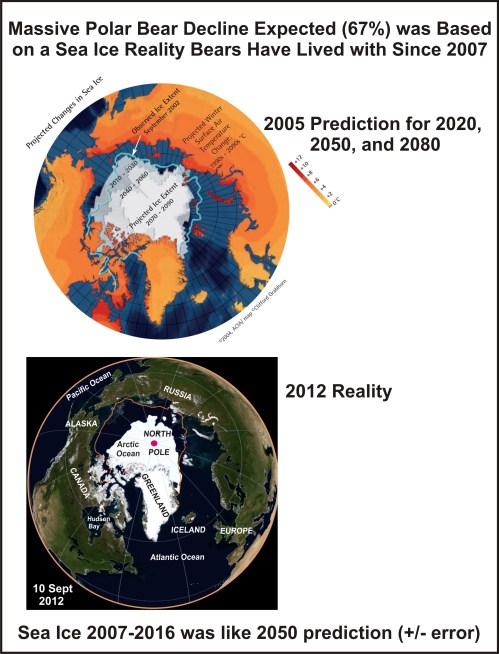
Polar bear specialists Ian Stirling and Steven Amstrup knew they didn’t have a valid argument to refute my paper (Crockford 2017; Crockford and Geist 2018) on their failed polar bear survival model (Amstrup et al. 2007), which their responses to my International Polar Bear Day (27 February 2018) Financial Post op-ed revealed to the world (see here and here with references).
So when ignoring me didn’t work – or, more accurately, when the world started paying too much attention to me, by their own admission (Harvey et al. 2018:3) – they teamed up with Michael Mann, Jeff Harvey, and Stephan Lewandowsky (all with previous form attacking colleagues who don’t share their views) to publish an academic paper attacking my scientific integrity. In the words of Terence Corcoran, I was “climate mauled.”
Judith Curry stated recently (14 February 2018), regarding the Mann lawsuit against Rand Simberg, Mark Steyn and the National Review vs. the attacks on her integrity:
“Mann’s libelous statements about me (because he is a scientist with many awards) are far more serious than say Rand Simberg’s statements about Mann.”
In other words, like the attack on me in the Harvey paper (used to libel other internet bloggers by association), when senior scientists like Mann, Stirling, and Amstrup use derogatory and defamatory language against a colleague it’s a serious breach of professional ethics that impacts careers. Harvey et al.’s attack against me may be worse than those against Curry at a Congressional Hearing because it has been entered into the scientific literature in my own field.1
However, I expect BioScience (read mostly by teachers, students, and the general public, and therefore widely subscribed to by public libraries) was the only outlet willing to publish such unprofessional tripe. The editor’s refusal to retract the paper after numerous complaints about the language and the quality of the scientific content, tells you all you need to know about the journal’s “low, sectarian standards“. For example, the notice showing the two corrections they were willing to make at the end of March 2018 had to be pulled because such an egregious error occurred (it was posted to the wrong journal) it got the attention of online watchdog Retraction Watch! [Still not fixed as of 8 April]

It also tells us quite a lot about the bias of its publishers, the American Institute of Biological Sciences.
Did you know, for example, that this organization has an “actionbioscience” program that provides free idealogically biased content aimed at kids and teachers that’s not particularly different from the biased content produced (without references) for kids and teachers by activist conservation outfit Polar Bears International (employer of Harvey et al. co-author Steve Amstrup)? The AIBS actionbioscience program currently includes an out-of date, alarmist essay by litigious Center for Biological Diversity employee Shaye Wolf on the plight of penguins (from 2009) as well as one by pessimistic polar bear specialist Andrew Derocher (from 2008) .
If you are able, please support the work I do here at PolarBearScience, some of which will go to Josh for these fabulous cartoons:

Here is a list of issues regarding the Harvey et al. paper as well as responses to it: some of these you won’t have heard before. Because this is a long summary post, for convenience I offer it here also in pdf form (latest version with a few typos/spelling errors corrected): “Climate mauling, polar bears, and self-inflicted wounds of the self-righteous.”
Continue reading

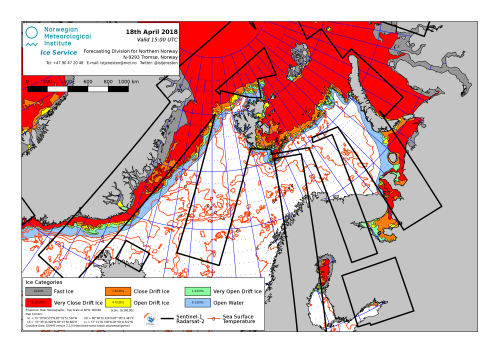


 “…absolutely the stupidest paper I have ever seen published” tweeted
“…absolutely the stupidest paper I have ever seen published” tweeted 












You must be logged in to post a comment.