It is now clear that the phenomenon of bears moving across Southern Beaufort Sea subpopulation boundaries compromised the US decision to list polar bears as ‘threatened’ and the IUCN Polar Bear Specialist Group (PBSG) knows that was the case.
subpopulation boundaries compromised the US decision to list polar bears as ‘threatened’ and the IUCN Polar Bear Specialist Group (PBSG) knows that was the case.
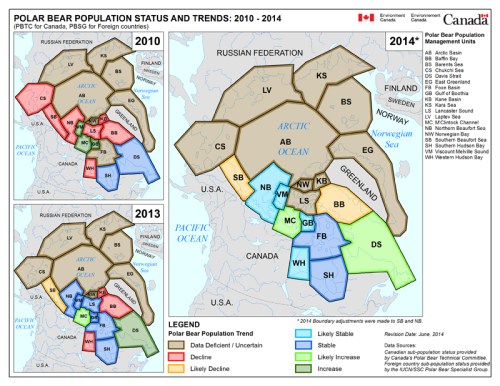
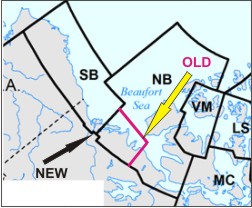
As I pointed out last week, the PBSG has admitted in their 2013 status table update (pdf here) that bears move around so much between the Chukchi Sea (CS), the Southern Beaufort (SB), and the Northern Beaufort (NB) subpopulations that major changes in the boundaries of the SB subpopulation are necessary (see Fig. 1 below).

Figure 1. From the paper by Amstrup and colleagues (2005) describing the effect that movement of bears across subpopulation boundaries has on setting harvest quotas and population estimates. Southern Beaufort (SB) boundary is solid red, Chukchi Sea (CS) is dashed yellow and Northern Beaufort (NB) is dotted light blue. “Point Barrow” is Barrow, AK (well inside the SB boundary). Click to enlarge.
Well, that’s not really news — changes to the SB boundaries were promised by the PBSG back in 2009 (Obbard et al. 2010), based on research by Steven Amstrup and colleagues published in 2001 and 2005. But now, in an astonishing admission, the PBSG have acknowledged that the last population survey for the SB (Regehr, Amstrup and Stirling, 2006), which appeared to register a decline in population size and reduced cub survival over time, did not take known movements of bears into account as it should have done.
In other words, that 2006 study almost certainly did not indicate bears dying due to reduced summer sea ice in the SB, as biologists said at the time — and which they presented as evidence that polar bears should be listed by the ESA as ‘threatened’ — but reflected capture of bears that were never part of the SB subpopulation and so moved out of the region.
As the PBSG said about the 2006 estimate:
“…it is important to note that there is the potential for un-modeled spatial heterogeneity in mark-recapture sampling that could bias survival and abundance estimates.” [my emphasis]
“Spatial heterogeneity” means that the sampled bears could have come from more than one population, a possibility which violates a critical requirement of the statistics used to generate the population and survival estimates. “Un-modeled” means that the ‘movement of bears’ problem was not factored into the mathematical models that generated the 2006 population size and survival estimates as it should have been.
Ecologist Jim Steele pointed some of this out in his book and his guest post last year, so it’s not news that this was done.
What’s shocking is that the PBSG have now admitted that the ‘movement of bears’ issue essentially invalidates the 2006 population estimate and the much-touted ‘reduced survival of cubs.’ The reduced survival of cubs data from that SB study was a critical component of the argument that US bears were already being negatively impacted by global warming and thus, should be listed as ‘threatened’ under the ESA (US Fish & Wildlife Service 2008).
Since the population decline and reduced survival is now acknowledged to be unfounded — and perhaps deliberately so — I ask you this: will a new SB survey — soon to be released by the same lead author (Eric Regehr) — undo the broken trust in US and PBSG polar bear biologists? Continue reading











You must be logged in to post a comment.