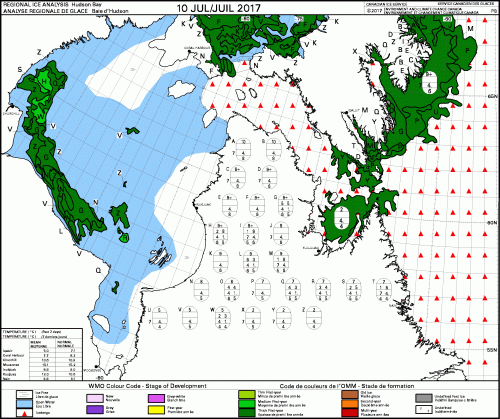
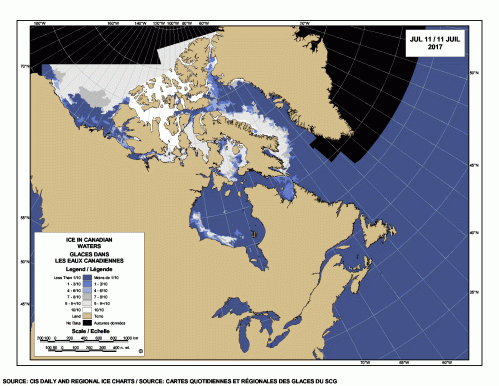
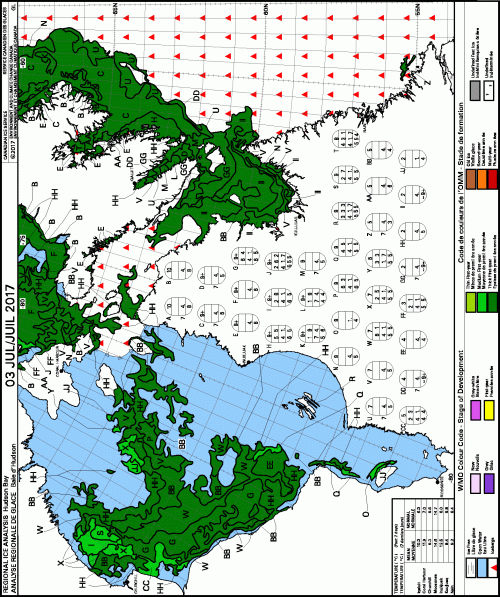
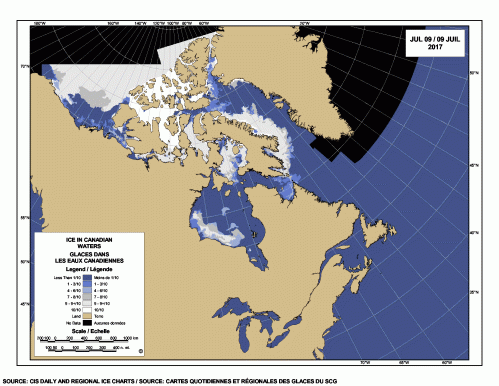
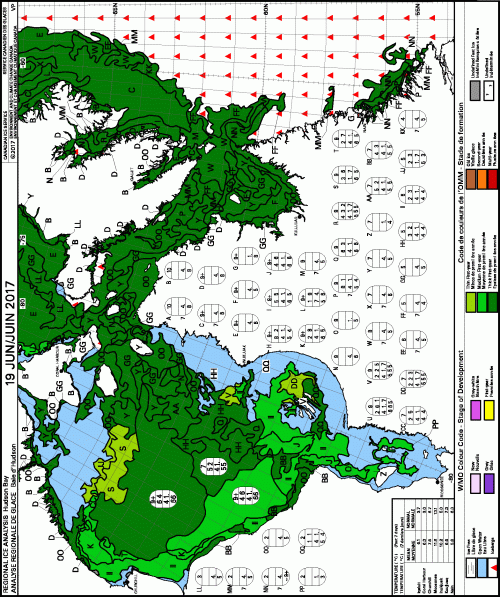
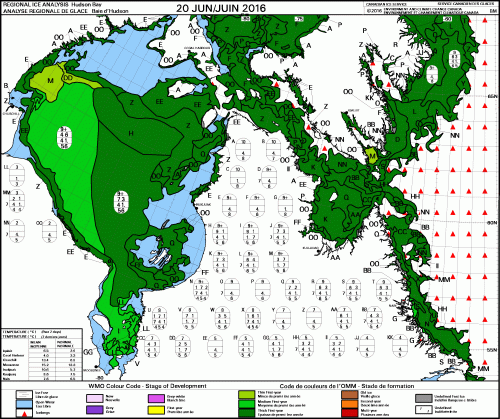
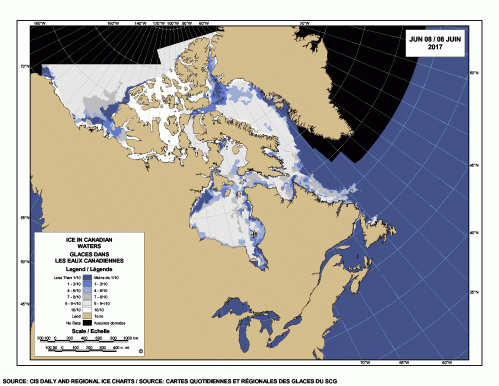
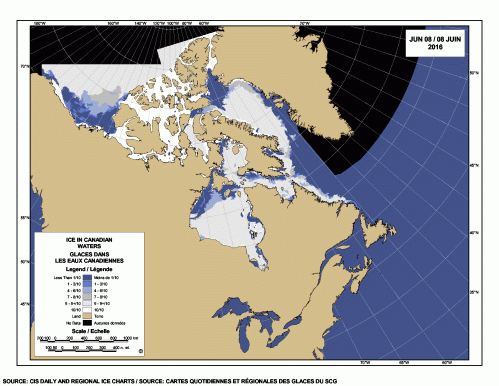
Yes, Arctic sea ice has declined since satellite records began in 1979 but polar bears have adjusted well to this change, especially to the abrupt decline to low summer sea ice levels that have been the norm since 2007.
Some polar bear subpopulations have indeed spent more time on land in summer than in previous decades but this had little negative impact on health or survival and while polar bear attacks on humans appear to have increased in recent years (Wilder et al. 2017), the reasons for this are not clear: reduced summer sea ice is almost certainly not the causal factor (see previous post here).
Ultimately, there is little reason to accept as plausible the computer models (e.g. Atwood et al. 2016; Regehr et al. 2016) that suggest polar bear numbers will decline by 30% or more within a few decades: even the IUCN Red List assessment (Wiig et al. 2015) determined the probability of that happening was only 70%.
Arctic sea ice has never been a stable living platform (Crockford 2015): it shifts from season to season, year to year, and millennia to millennia. Without the ability to adapt to changing conditions, Arctic species like polar bears and their prey species (seals, walrus, beluga, narwhal) would not have survived the unimaginably extreme changes in ice extent and thickness that have occurred over the last 30,000 years, let alone the extremes of sea ice they endured in the last 200,000 years or so.
Some biologists continue to hawk doomsday scenarios for polar bears due to summer sea ice loss but the truth is that their previous predictions based on sea ice declines failed so miserably (e.g. Amstrup et al. 2007) that it’s impossible to take the new ones seriously — especially since the basic assumptions that caused the first predictions to fail have not been corrected, as I’ve stated in print (Crockford 2017:27):
In summary, recent research has shown that most bears are capable of surviving a summer fast of five months or so as long as they have fed sufficiently from late winter through spring, which appears to have taken place since 2007 despite marked declines in summer sea ice extent.
The assumption that summer sea ice is critical feeding habitat for polar bears is not supported.
Recent research shows that changes in summer ice extent generally matter much less than assumed in predictive polar bear survival models of the early 2000s as well as in recent models devised to replace them (Amstrup et al. 2010; Atwood et al. 2016a; Regehr et al. 2015; Regeher et al. 2016; Wiig et al. 2015), while variations in spring ice conditions matter more.
As a consequence, the evidence to date suggests that even if an ‘ice-free’ summer occurs sometime in the future defined as sea ice extent of 1 million km2 or less (Jahn et al. 2016) it is unlikely to have a devastating impact on polar bears or their prey. [my bold]
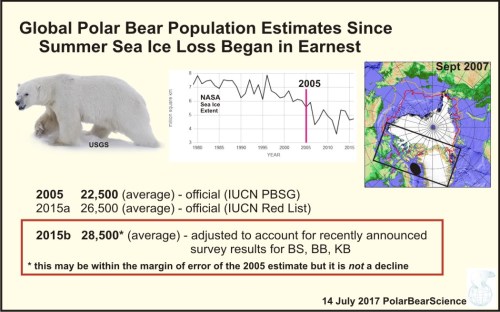
The abrupt drop in summer sea ice that occurred in 2007 was not predicted by experts to occur until mid-century yet the predicted decimation of polar bears worldwide expected under those conditions (a loss of 2/3 of the global total, to only about 6660-8325 bears) not only did not happen, it did not come even close to happening (Crockford 2017; see also my recent books, Polar Bear Facts & Myths, and Polar Bears: Outstanding Survivors of Climate Change, sidebar).
Instead, the global population grew from about 22,550 bears in 2005 to about 28,500 bears in 2015. And while this might not be a statistically significant increase (due to the very wide margins of error for polar bear estimates), it is absolutely not a decline.
The present reality is that low summer sea ice cover since 2007 has not caused polar bear numbers to decline and therefore, polar bears are not a species in trouble. This suggests that even if the Arctic should become briefly ice-free in summer in the future, polar bears are likely to be only minimally affected and not become threatened with extinction. Polar bears are outstanding survivors of climate change: recent research and their evolutionary history confirm this to be true.
Continue reading

 The photos were taken by Churchill photographer and guide Alex De Vries on Thursday 13 July and I hope he doesn’t mind my including one of those here as documentary evidence of the good body condition of this mother and both her cubs — see more photos at the Churchill Polar Bears blog post dated 14 July here.
The photos were taken by Churchill photographer and guide Alex De Vries on Thursday 13 July and I hope he doesn’t mind my including one of those here as documentary evidence of the good body condition of this mother and both her cubs — see more photos at the Churchill Polar Bears blog post dated 14 July here.













You must be logged in to post a comment.