[Update October 14, 2013: correction regarding Davis Strait population estimate, noted below]
I heard via the grapevine that the IUCN Polar Bear Specialist Group (PBSG) meeting, tentatively slated to be held this July (Obbard et al. 2010), has been postponed until 2014. [That will be the 16th Working Meeting, as they are called]
Word has it that shifting the meeting forward will allow the group time to put together a new population estimate that will incorporate recent survey results.
So which subpopulations are slated to be updated?
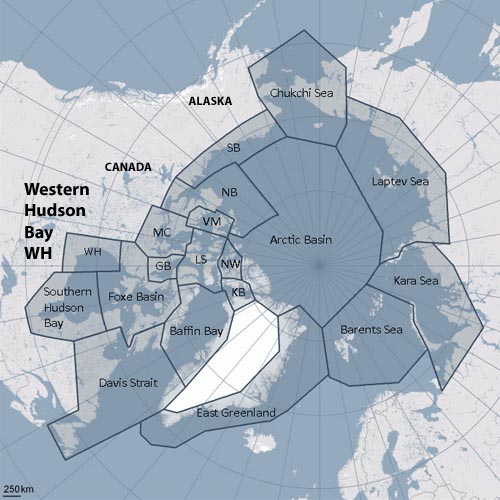
Polar bear subpopulations defined by the Polar Bear Specialist Group (PBSG). Courtesy the PBSG.
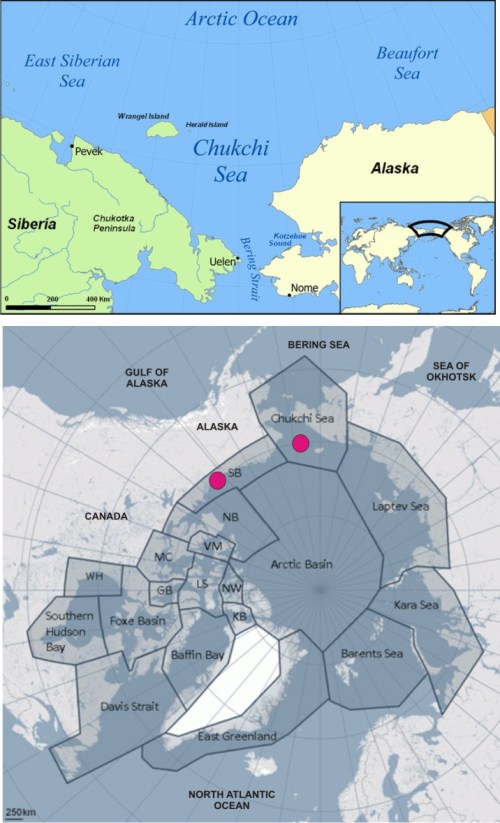
As far as I can determine, there are at least two that haven’t quite been finished: Baffin Bay and Southern Beaufort. The Baffin Bay survey was supposed to be completed this spring, so the numbers just need to be crunched. Southern Beaufort has a survey in progress, planned to continue through the fall of 2013.
Here are some comments on the 2012 Southern Beaufort field season (USFWS Newletter 2013:17):
“The number of polar bears observed in 2012 was high relative to similar surveys conducted over the past decade. During August and September surveys, the majority of bears were observed east of Prudhoe Bay, primarily near Kaktovik. Body condition appeared relatively normal for this time of year with most bears reported to be in average condition.” [my bold] [see previous post here re: Kaktovik bears]
There are new counts for Foxe Basin (estimated at ~2,580 bears, similar to the early 1990s estimate of ~2,200; Stapleton, Peacock and Garshelis 2012) and Western Hudson Bay (estimated at ~1,000 bears, similar to the 2004 estimate of ~935; Stapleton, Atkinson et al. 2012) based on aerial surveys. These numbers have not yet been incorporated into the global total, although the studies suggest both of those populations have been stable since the last survey.
CBC News (June 26, 2012):
“A study has found that the polar bear population in the Foxe Basin region of Nunavut is stable and the bears are in good health.
The territorial government did an aerial survey of the bear population in 2009 and 2010. The survey results show the population is about the same size as it was in 1990 – about 2,580 bears.” [my bold]
There is also the new population estimate for Davis Strait (Peacock et al. 2013) that needs to be incorporated into the global total – in this case, there has been an increase from the previous estimate (up from ~1,400 to ~2,158). [corrected Oct. 14 2013] The population increase for Davis Strait has already been incorporated into the current global estimate. The new numbers were available by 2009 (the time of the last PBSG meeting) but the peer-reviewed publications (with all of the pertinent details) were not produced until recently (2012-2013, discussed here and here).
Continue reading











You must be logged in to post a comment.